
For example, Dalton’s atomic theory was an attempt to explain the results of measurements that allowed him to calculate the relative masses of elements combined in various compounds. We can argue that modern chemical science began when scientists started exploring the quantitative as well as the qualitative aspects of chemistry. Define the amount unit mole and the related quantity Avogadro’s numberĮxplain the relation between mass, moles, and numbers of atoms or molecules, and perform calculations deriving these quantities from one another.Calculate formula masses for covalent and ionic compounds.
Earlier, we found the molar mass of CO 2 to be 44.01 g/mol.īy the end of this section, you will be able to:

Solution: We use dimensional analysis and the the molar mass of carbon dioxide to solve this problem. Problem: How many grams are in 0.762 mol of CO 2?
#Xee molar mass how to
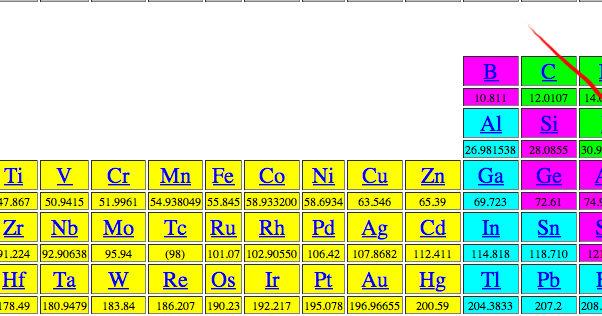
Likewise, now that we know how to determine molar masses for molecules, we can use this to solve problems, too. Solution: We use dimensional analysis and an equivalent term for Avogadro’s number to solve this problem. Problem: How many atoms are in 2.15 mol of solid sodium metal? Now that we’ve seen Avogadro’s number, we can use this value to solve problems. + 2 x (molar mass of O atoms) = 2 x (16.00 g/mol) = 32.00 g/molĤ4.01 g/mol Using Avogadro’s Number in Calculations How do we determine the molar masses of molecules? We do this by adding up the molar masses of all the atoms that comprise that molecule.Ģ x (molar mass of O atoms) = 2 x (16.00 g/mol) = 32.00 g/molġ x (molar mass of C atoms) = 1 x (12.01 g/mol) = 12.01 g/mol Molar masses of atoms are found directly on the periodic table. We use the term molar mass to describe how many grams are in one mole of a substance.
1 moles of atoms = 6.022 x 10 23 atoms (Avogadro’s number, N A). the mass of one mole of carbon atoms is 12.011 grams. the average atomic mass for a single carbon atom is 12.011 amu. Using the chemical formula of the compound and the periodic table of elements, we can add up the atomic weights and calculate molecular weight of the substance.As a recap, the periodic table provides average masses for every element, and from this we can state: These relative weights computed from the chemical equation are sometimes called equation weights. For bulk stoichiometric calculations, we are usually determining molar mass, which may also be called standard atomic weight or average atomic mass.įormula weights are especially useful in determining the relative weights of reagents and products in a chemical reaction. This is not the same as molecular mass, which is the mass of a single molecule of well-defined isotopes. This is how to calculate molar mass (average molecular weight), which is based on isotropically weighted averages. The atomic weights used on this site come from NIST, the National Institute of Standards and Technology. This site explains how to find molar mass. The reason is that the molar mass of the substance affects the conversion. To complete this calculation, you have to know what substance you are trying to convert. The percentage by weight of any atom or group of atoms in a compound can be computed by dividing the total weight of the atom (or group of atoms) in the formula by the formula weight and multiplying by 100.Ī common request on this site is to convert grams to moles. If the formula used in calculating molar mass is the molecular formula, the formula weight computed is the molecular weight. The formula weight is simply the weight in atomic mass units of all the atoms in a given formula. When calculating molecular weight of a chemical compound, it tells us how many grams are in one mole of that substance. In chemistry, the formula weight is a quantity computed by multiplying the atomic weight (in atomic mass units) of each element in a chemical formula by the number of atoms of that element present in the formula, then adding all of these products together.įinding molar mass starts with units of grams per mole (g/mol).







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
